METHODICAL BASICS OF THERMOVISION TOMOGRAPHY
1METHODICAL BASICS OF THERMOVISION TOMOGRAPHY
INITIAL INFORMATION FOR TVT
multispectral images of the MODIS and Landsat spacecraft, terrain, sea bathymetry, etc
KIND OF THERMOVISION SURVEY
space, aviation, instrumental on ground
OBJECT OF STUDY
continent, sea shelf, underground mining
SOLVABLE GEOPHYSICAL PROBLEMS
• regional study of the lithosphere
• search for hydrocarbon deposits
• search for underground fresh waters
• search for ore deposits
• search for geothermal heat sources
• environmental monitoring of objects
COMPREHENSIVE INTERPRETATION OF MATERIALS
TVT + seismic survey | TVT + electrical prospecting / magnetometry / gravimetry |
TVT + well thermometry, etc.
2METHODICAL BASICS
PROCESSING OF THERMOVISION MATERIAL
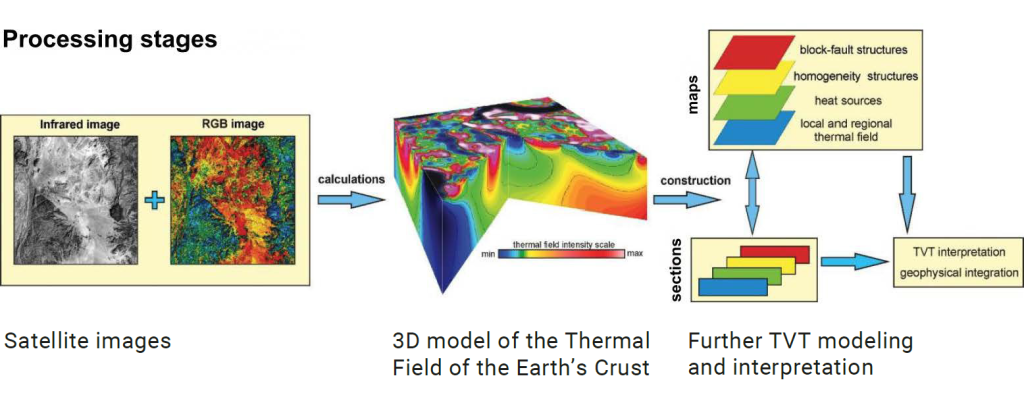
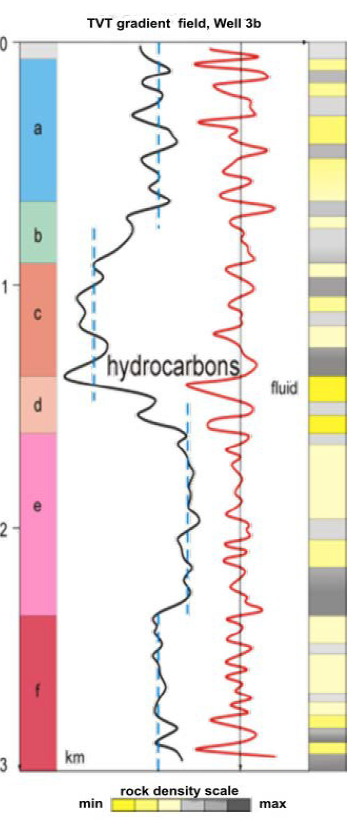
Characteristics of the thermal field in the well
3 MATHEMATICAL ALGORITHMS FOR TVT CALCULATIONS
Field source function
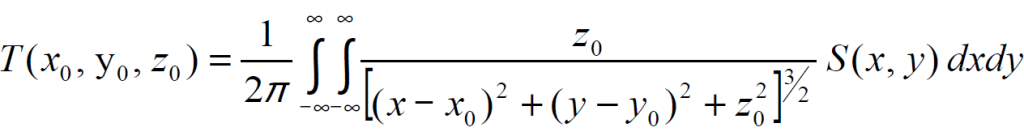
x and y – coordinates along the surface of the boundary plane;
x0, y0, z0 – coordinates for the volume of the lower half-space.
Convolution with Gauss core
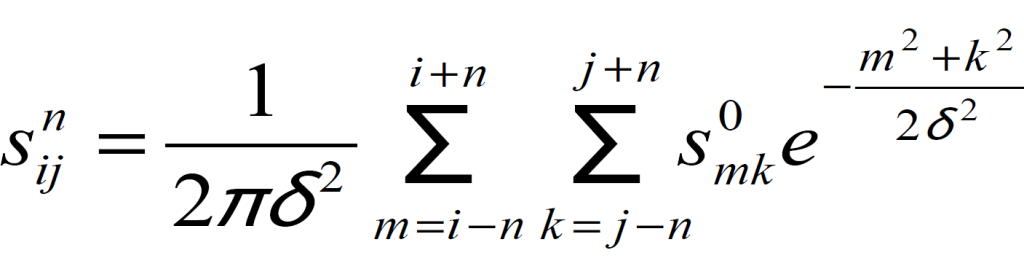
snij – layer element at depth n with coordinates ( i, j);
sOmk – element of the original image with coordinates ( m, k).
hn = k•n•δxy
n – layer number; hn – layer depth n;
δxy – spatial resolution of the image.
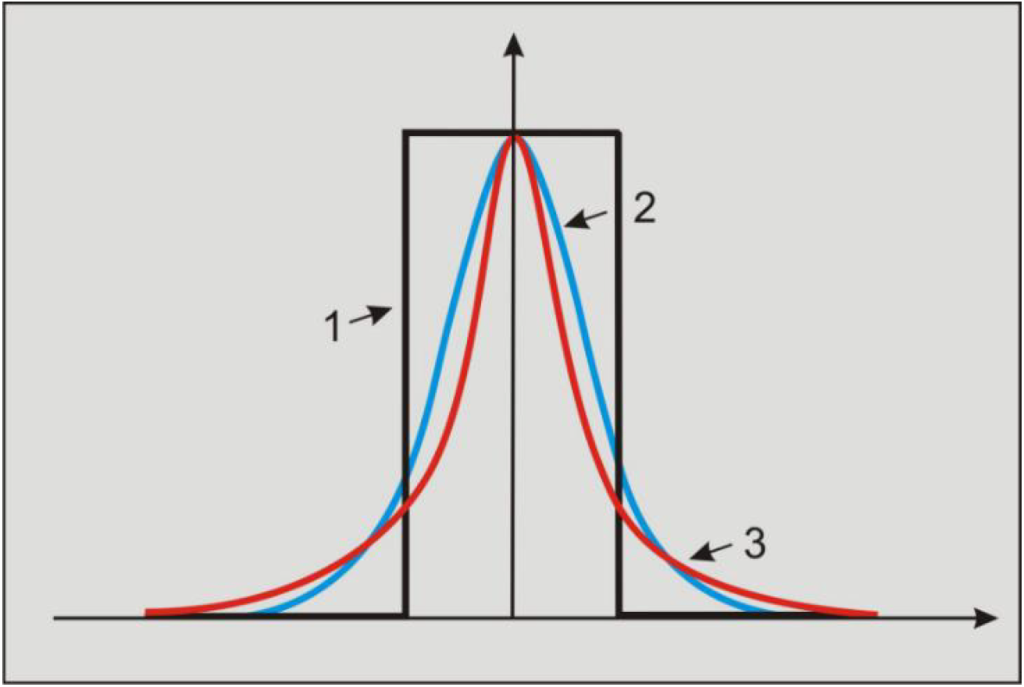
Graphs of the convolution cores for:
1—averaging, 2—with a Gaussian core, 3—source functions
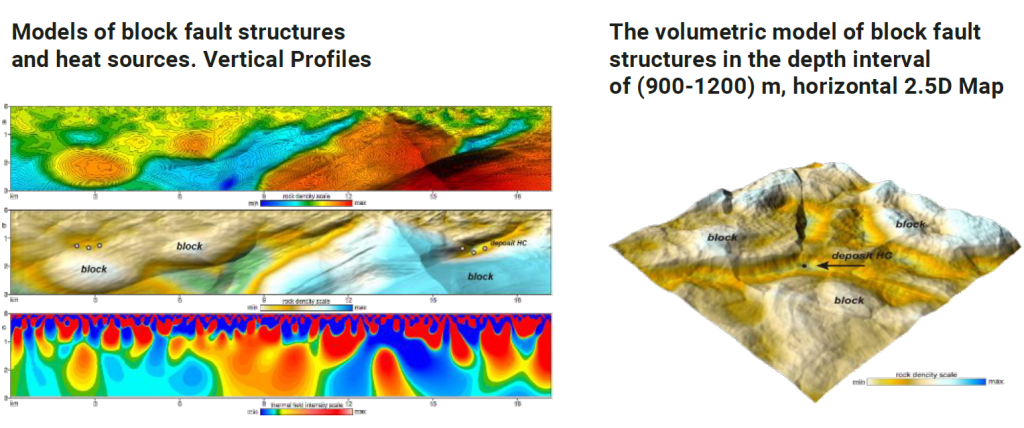
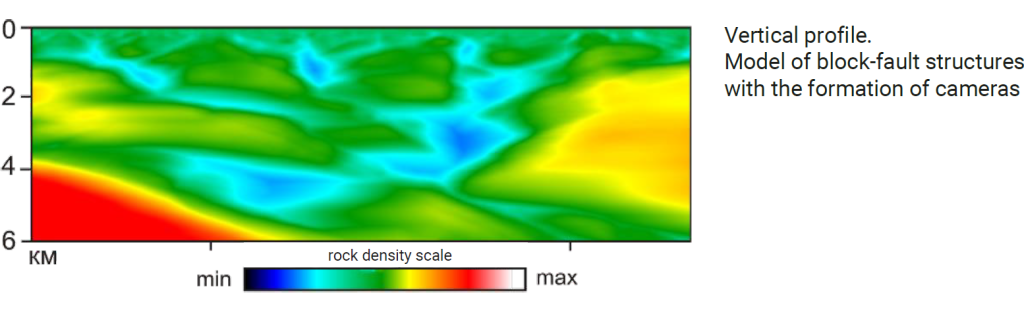
4 Calculation of the volumetric model of block-fault structures:
Calculation of the volumetric model of thermal field homogeneity:

Calculation of the volumetric model of thermal field homogeneity:
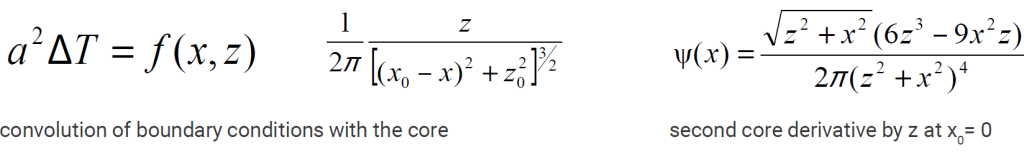

5 EXAMPLES OF TVT MODE LS OF THE E ARTH’S СRUST STRUCTURES (MAPS, VERTICAL PROFILES), WHICH ARE CALCULATED IN ACCORDANCE WITH THE ABOVE FORMULAS AND ALGORITHMS.
Map-sections of block-fault structures at depths of 2, 6 and 10 km
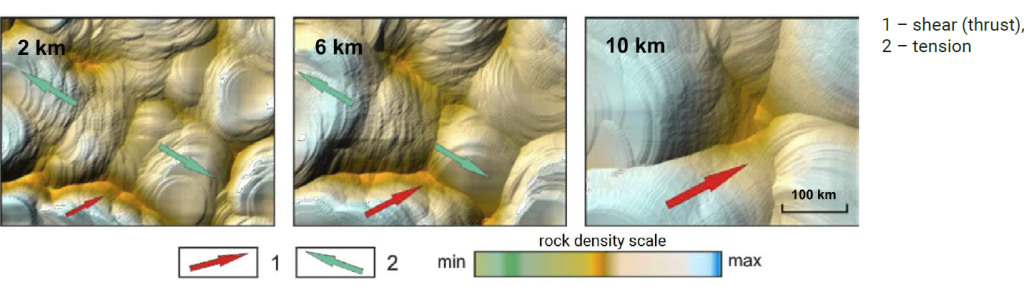
6GRAPHIC IMAGES
VERTICAL PROFILE. MODEL OF FAULTS AND FRACTURES IN CRUSTAL STRUCTURES

Vertical Profile, block-fault structure in monochrome color. The fault tectonics of the section is clearly visible (faults are colored gray-black, dense rocks are white).
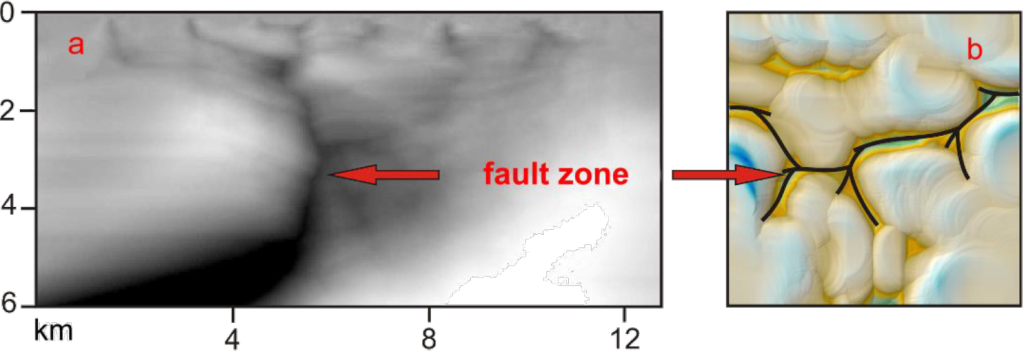
View of fault tectonics in the vertical section (a) and on the map of blocks (b)
7 STRUCTURAL VIEW OF THE FORMATION OF GRABEN AND HORST ALONG THE BASEMENT
Vertical TVT Profile
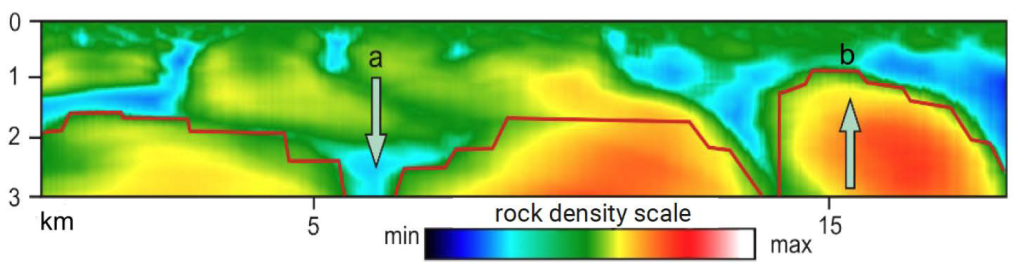
Length – 18 km, depth – 3 km. Block-fault structures.
Dense rocks are colored red and yellow, decompacted rocks are green and blue.
Arrow (a) points to Graben, arrow (b) to Horst.
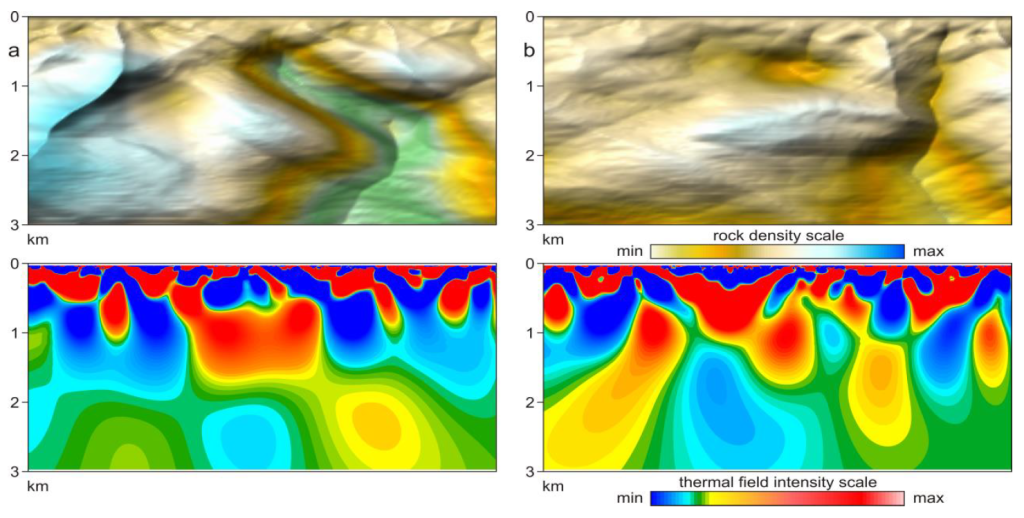
8 SEISMIC AND TVT MODELS OF A SALT DOME STRUCTURE. MEXICAN OIL PROVINCE.
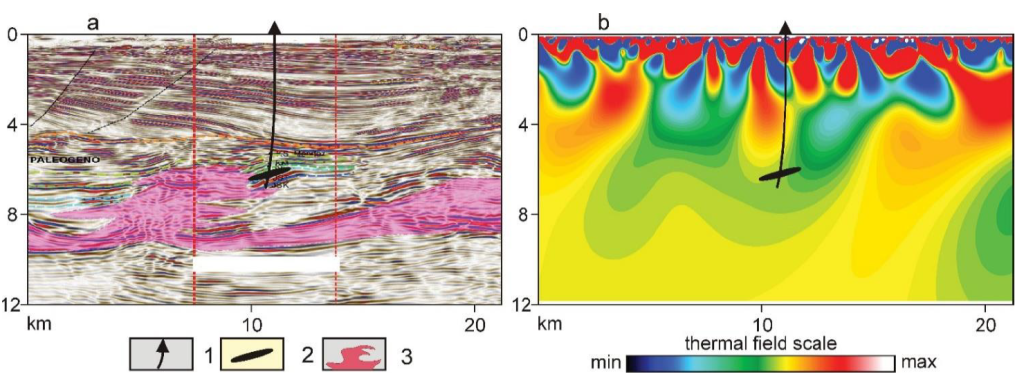
Seismic section (a)
and TVT model of heat sources (b)
in the zone of development of the salt dome
Legend:
1. Mayacaste-1 well;
2. Oil reservoir;
3. Salt-dome structure
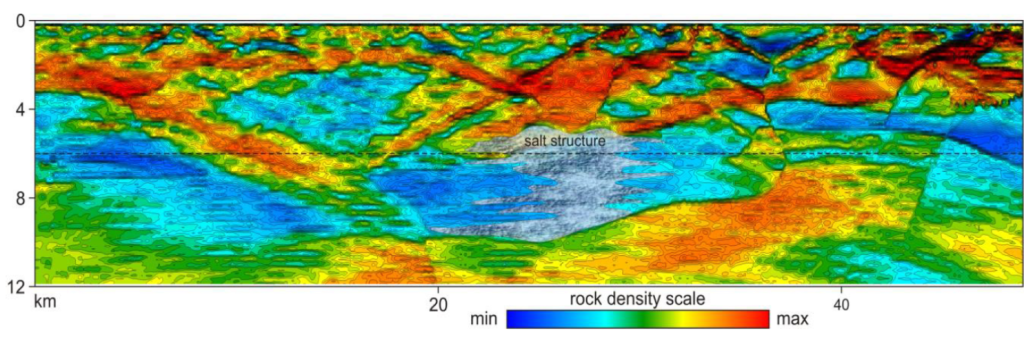
TVT vertical profile.
TVT model of block-fault structures
and a salt dome (image center, gray color)
in a sedimentary cover.
9CLASSIFICATION OF TVT MODELS BY THE LOCATION OF THE AXIS OF GEOLOGICAL STRUCTURES.
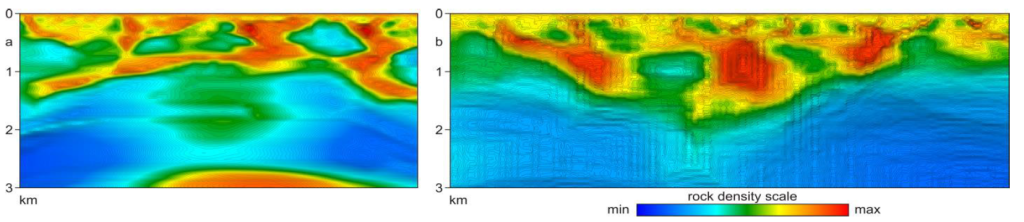
a - convex, reservoir
b - concave, local isometrice
Models of symmetric vertical natural structures
a - mono-axial (fan-shaped),
b - two axial (combined)
View of models of asymmetric natural structures
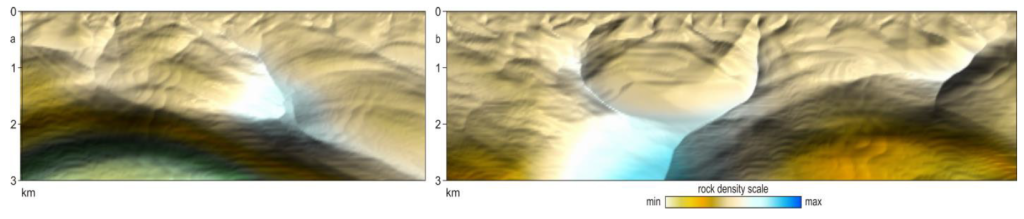
a - left-handed
b - right-handed inclined axis
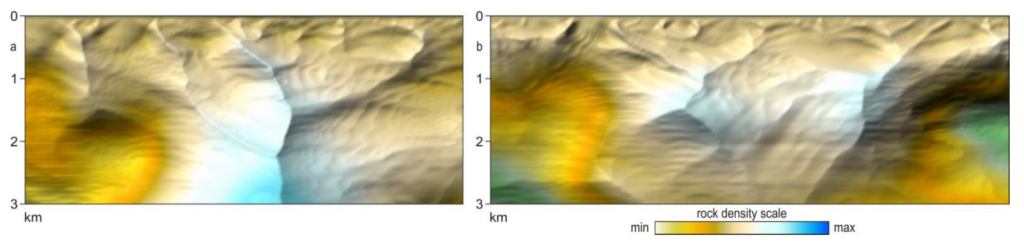
10CLASSIFICATION OF NATURAL HYDROTHERMAL RESERVOIRS
Traps are formed as a result of structural changes in reservoir rocks.
A natural reservoir can be a volumetric, linear (with a slightly inclined or vertical plane) or complex-built chambers.
A complexly constructed trap should be understood as a combination of various volumetric and linear chambers, interconnected by local permeable zones.
Natural closed reservoirs in the model of block-fault structures
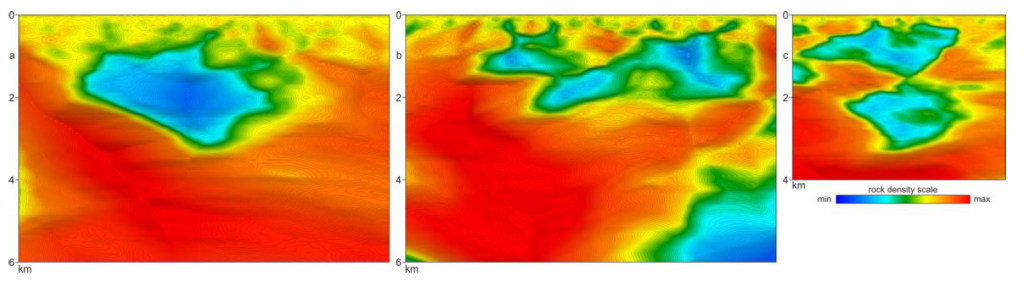
a - volumetric (closed),
b - horizontal-linear,
c - complex-built (combined)
